Projects

Accelerate Science
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to become an engine for scientific discovery across disciplines – from predicting the impact of climate change, to using genetic data to create new healthcare treatments, and from finding new astronomical phenomena to identifying new materials here on Earth.

The AI Council
The UK AI Council was an independent committee that provided advice on AI policy and strategy to the UK Government from 2018 – 2023. In 2022-23, the Council convened a series of discussions focused on the policy implications of advances in Large Language Models, with the aim of supporting rapid Government action to build national capability in Foundation Models.

AutoAI
While excitement about the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies continues to build, a gap is emerging between our aspirations for the benefits of AI and our ability to deploy these technologies to tackle real-world challenges.

The Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation
The CDEI is a government expert body enabling the trustworthy use of data and AI. Its multidisciplinary team of specialists, with expertise in data and AI policy, public engagement, computational social science and software engineering, are supported by an advisory board of world-leading experts to deliver, test and refine trustworthy approaches to data and AI governance, working with organisations across the UK.

Challenges in machine learning deployment
In addition to being a thriving academic discipline, machine learning is increasingly adopted as a solution to real world business problems. But underneath this seeming success lies a chasm of failures. This project studies reports of ML deployment, and investigates issues practitioners face at each step of the ML deployment pipeline
Climate Ensembling
General Circulation Models (GCMs) of Earth's climate provide robust simulations of large-scale average climatic variables, such as end-of-century global average temperature, under various future greenhouse gas emissions scenarios. Translating these outputs to insights that can be used to manage the local-level impacts of climate change is challenging, and requires innovations in modelling, data management, and software engineering.

Data-Oriented Architectures for AI-based Systems
Data Oriented Architecture (DOA) is a software architecture pattern that creates data-driven, loosely coupled, decentralised, and open systems. DOA achieves these goals by exposing systems' data as first class citizen to distributed, stateless, and asynchronous systems’ components. These design decisions enable DOA-based systems to achieve desirable properties such as data availability, reusability, and monitoring, as well as systems adaptability, scalability, and autonomy.
Data sharing in Africa: lessons from COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic intensified the need for timely and accurate data to inform policymaking. Countries across Africa have developed, and are still developing, innovative uses of data and statistics to monitor the extent of the spread of COVID-19 among their populations. Drawing from real-world examples, this projects the lessons offered by these innovations for future data policy frameworks.

Data Trusts Initiative
Reaping the benefits of data and digital technologies will require robust new institutions or frameworks that can allow data sharing - helping develop new data-enabled products and services - while protecting individual rights and freedoms. Data trusts offer a mechanism to achieve this goal through participatory data stewardship.
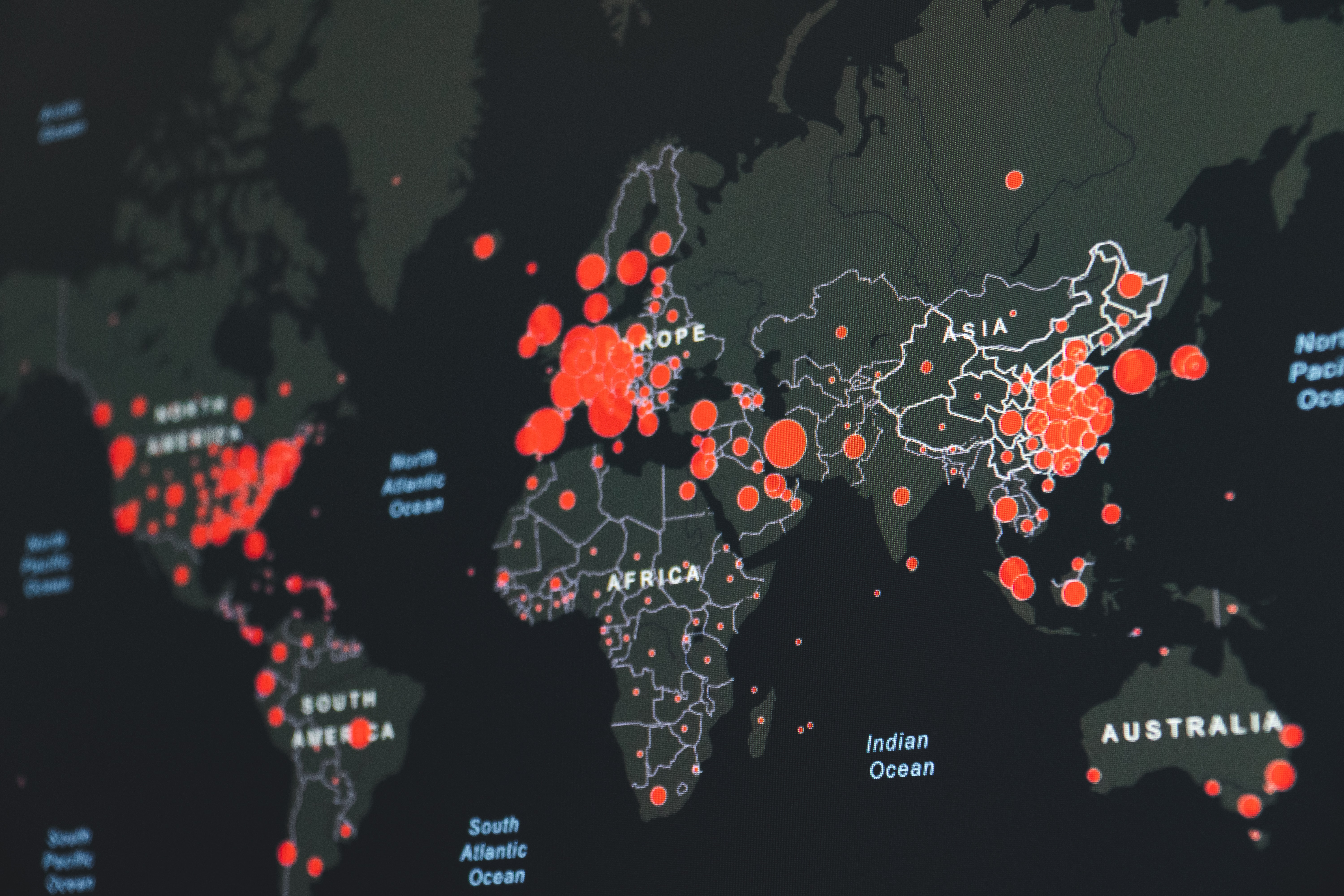
DELVE (Data Evaluation and Learning for Viral Epidemics)
DELVE is a multi-disciplinary group, convened by the Royal Society, to support a data-driven approach to learning from the different approaches countries are taking to managing the pandemic. DELVE operated through 2020, providing advice to the UK Government and SAGE.

European Network of AI Excellence Centres
European Learning and Intelligence Systems Excellence (ELISE) is a consortium of artificial intelligence (AI) research hubs that connects Europe’s leading researchers in machine learning and AI.

Evaluation of dataflow for ML deployment
When deploying machine learning algorithms in real-world systems, software developers face a new set of challenges. This project asks: "What are the underlying reasons for these challenges to arise?", and proposes that the problem lies with the modern trend of building software systems as microservices.
Human Cell Atlas
The Human Cell Atlas programme aims to chart the properties of human cells, building a reference map of the human body that can be used to understand human health and to treat disease.